Realidad Virtual y manejo del dolor en pacientes neurológicos
Dynamics VR – 21/07/2025
Índice de contenidos
- 1. Frecuencia del dolor en condiciones neurológicas
- 2. Procesamiento del dolor y la toma de decisiones motoras
- 3. ¿Cómo puede ayudar Dynamics VR?
Frecuencia del dolor en condiciones neurológicas
El dolor es una de las secuelas más prevalentes y debilitantes en los trastornos neurológicos, afectando de forma significativa la calidad de vida de los pacientes:
- ICTUS: El dolor se presenta en un rango amplio del 19% al 74% de los casos, siendo el hombro la localización más frecuente, con una prevalencia estimada entre el 11% y el 40% (Kim, 2009).
- TRAUMATISMO CRANEOENCEFÁLICO (TCE): El dolor crónico afecta al 51,5% de los pacientes, mientras que el dolor agudo es común en las primeras semanas tras el trauma, relacionado con el daño tisular (Irvine & Clark, 2018).
- PÁRKINSON: Hasta un 85% de los pacientes reportan algún tipo de dolor, el cual tiende a empeorar con la progresión de la enfermedad y genera un impacto económico considerable (Naisby et al., 2021).
- ALZHÉIMER: La prevalencia de dolor crónico se sitúa en torno al 45,8%, aunque con frecuencia es infradiagnosticado debido a la dificultad de los pacientes para comunicarlo. Además, se han observado alteraciones neurológicas similares al dolor crónico idiopático, como disfunciones en el sistema noradrenérgico, activación microglial y aumento de la neuroinflamación en la corteza frontal (Cao et al., 2019).
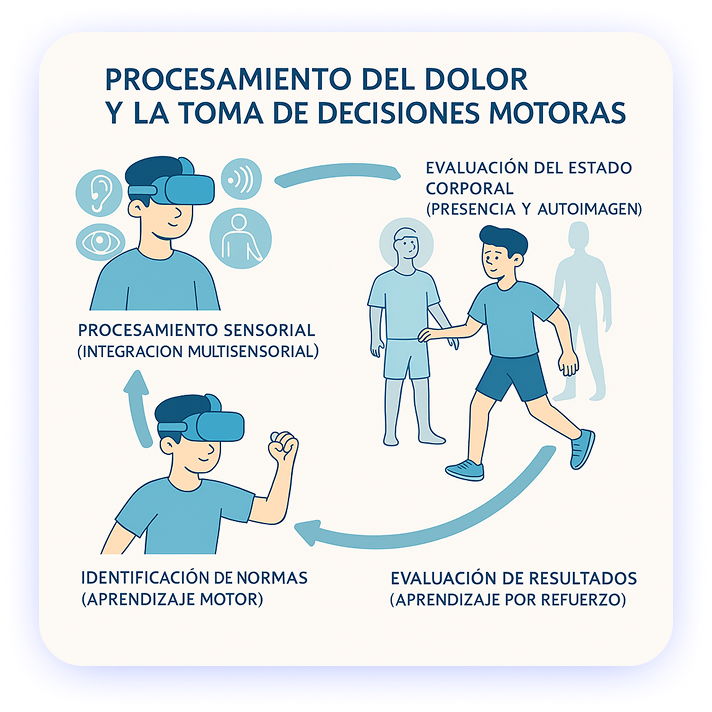
Procesamiento del dolor y la toma de decisiones motoras
Una rehabilitación activa y efectiva requiere comprender cómo el dolor crónico influye en el comportamiento motor y en la toma de decisiones. Según el modelo dinámico propuesto por Guerra-Armas et al. (2023), las intervenciones inmersivas con Realidad Virtual pueden influir positivamente en las siguientes etapas del procesamiento del dolor:
1. Procesamiento sensorial (integración multisensorial)
En muchas condiciones neurológicas, la integración de estímulos sensoriales está alterada. La RV permite modular la relevancia de estos estímulos (visuales, auditivos, hápticos), y adaptarlos al perfil sensitivo del paciente, facilitando una experiencia más coherente y eficaz (Kamari et al., 2024; Ferrer-Costa et al., 2025).
2. Evaluación del estado corporal (presencia y autoimagen)
La inmersión en entornos virtuales permite modificar la percepción del cuerpo y del entorno mediante la creación de ilusiones corporales (como avatares de cuerpo completo), aprovechando el funcionamiento de las neuronas espejo para influir en la percepción del dolor (Drakenberg et al., 2023).
3. Identificación de normas (aprendizaje motor)
La congruencia entre los movimientos del usuario y su avatar facilita un nuevo proceso de aprendizaje motor, reforzando patrones funcionales que ayudan a reducir conductas compensatorias relacionadas con el dolor.
4. Evaluación de resultados (aprendizaje por refuerzo)
Al cambiar la interpretación de los estímulos dolorosos, el paciente puede experimentar nuevas formas de moverse en distintos entornos. La práctica repetitiva de tareas funcionales en estos escenarios virtuales facilita la reorganización neuromotora y el control del movimiento, con beneficios tanto físicos como cognitivos.
¿Cómo puede ayudar Dynamics VR ?
La solución de Dynamics VR integra entornos inmersivos diseñados específicamente para el abordaje del dolor en pacientes neurológicos, combinando tareas funcionales repetitivas, feedback visual en tiempo real y estrategias cognitivas adaptadas al perfil clínico.
Gracias a sus escenarios interactivos y la posibilidad de personalizar los ejercicios según el nivel funcional y sensorial del paciente, Dynamics favorece la activación motora sin generar amenaza, reduciendo así el círculo vicioso dolor-miedo-inactividad. Además, permite al terapeuta monitorizar en tiempo real la respuesta del paciente, ajustar los estímulos y promover aprendizajes motores positivos.
En definitiva, Dynamics VR no solo ofrece una herramienta terapéutica innovadora, sino también una vía eficaz y motivadora para reducir el dolor y mejorar la funcionalidad en poblaciones neurológicas complejas.
Tal vez te interese...

Por Dynamics VR l 17 Julio, 2025.
Evidencia de la Realidad Virtual en Daño cerebral Adquirido
El Daño Cerebral Adquirido (DCA) es una lesión que aparece en el cerebro después del nacimiento, y que no es hereditaria, congénita ni degenerativa. Puede surgir de forma traumática, como en accidentes de tráfico o caídas…

Por Dynamics VR l 21 Julio, 2025.
Evidencia de la Realidad Virtual en Daño cerebral No Adquirido
El daño cerebral no adquirido hace referencia a aquellas alteraciones neurológicas presentes desde el nacimiento o desarrolladas a lo largo de la vida como consecuencia de procesos genéticos o enfermedades…

